Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Gregorian Calendar: A Brief History
- 3.2 The Structure of the Gregorian Calendar
- 3.3 The Significance of the Calendar in the United States
- 3.4 Understanding Time Zones in the United States
- 3.5 Calendar-Based Holidays in the United States
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Using the Calendar Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide

The United States, like many other nations, adheres to the Gregorian calendar, a system of timekeeping that has become the international standard. This calendar, with its familiar arrangement of months, weeks, and days, plays a crucial role in organizing our lives, from personal schedules to national events. This guide delves into the intricacies of the calendar in the United States, exploring its history, structure, and significance.
The Gregorian Calendar: A Brief History
The Gregorian calendar, named after Pope Gregory XIII, who introduced it in 1582, is a solar calendar. This means it is based on the Earth’s revolution around the sun, with each year consisting of approximately 365.2422 days. The calendar features a leap year every four years, with the exception of years divisible by 100 but not by 400, to account for the extra quarter day.
Before the Gregorian calendar, Europe primarily used the Julian calendar, which overestimated the length of a year, leading to a discrepancy of approximately 11 minutes. This discrepancy resulted in a drift of the calendar year from the actual solar year, causing the vernal equinox (the beginning of spring) to occur earlier in the calendar year. The Gregorian calendar addressed this drift by introducing a more accurate leap year system.
The Structure of the Gregorian Calendar
The Gregorian calendar consists of 12 months, each with a specific number of days:
- January: 31 days
- February: 28 days (29 in leap years)
- March: 31 days
- April: 30 days
- May: 31 days
- June: 30 days
- July: 31 days
- August: 31 days
- September: 30 days
- October: 31 days
- November: 30 days
- December: 31 days
The calendar also divides each year into four quarters, with each quarter comprising three months. The calendar week consists of seven days, starting with Sunday and ending with Saturday.
The Significance of the Calendar in the United States
The calendar plays a pivotal role in American society, influencing various aspects of life, including:
- Government and Legal Systems: The calendar defines deadlines for legal proceedings, tax filing, and elections.
- Business and Commerce: Businesses rely on the calendar to schedule meetings, plan product launches, and manage inventory.
- Education: The calendar determines the academic year, school holidays, and exam schedules.
- Personal Life: Individuals use the calendar to manage appointments, plan vacations, and track birthdays and anniversaries.
- Cultural Events: The calendar marks significant national holidays and cultural celebrations, fostering a sense of shared identity.
Understanding Time Zones in the United States
The United States spans multiple time zones, each with its own standard time. This is due to the country’s vast geographical expanse. There are four standard time zones in the contiguous United States:
- Eastern Time Zone (ET): Covers the easternmost states, including New York, Florida, and Pennsylvania.
- Central Time Zone (CT): Covers the central states, including Texas, Illinois, and Minnesota.
- Mountain Time Zone (MT): Covers the western states, including Colorado, Arizona, and Utah.
- Pacific Time Zone (PT): Covers the westernmost states, including California, Oregon, and Washington.
Additionally, Alaska and Hawaii have their own time zones. Understanding time zones is crucial for scheduling meetings, making phone calls, and coordinating events across different regions of the United States.
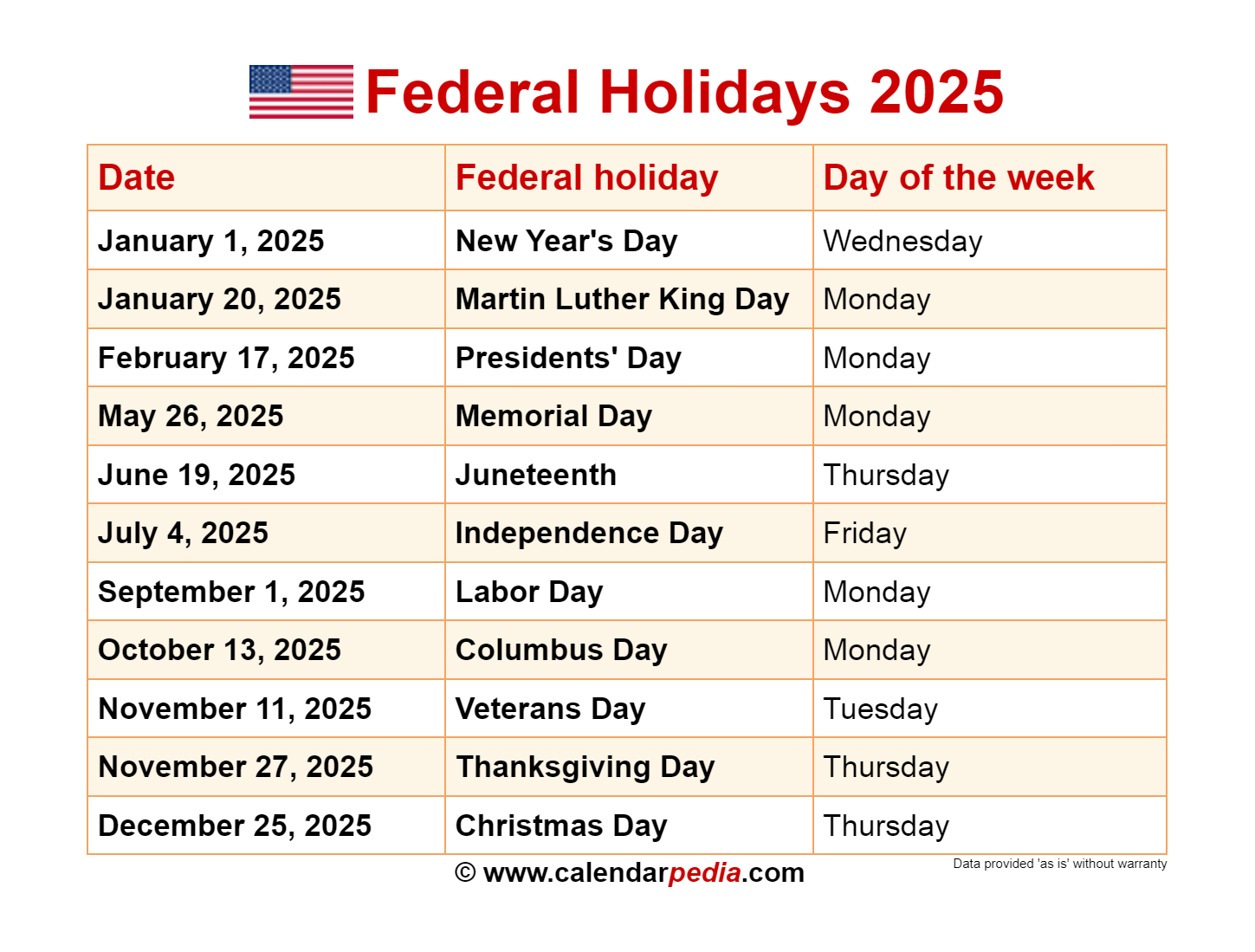
Calendar-Based Holidays in the United States
The United States observes numerous holidays throughout the year, many of which are rooted in its history and culture. Some of the most prominent holidays include:
- New Year’s Day (January 1): Celebrates the beginning of a new year.
- Martin Luther King Jr. Day (Third Monday in January): Honors the civil rights leader.
- Presidents’ Day (Third Monday in February): Celebrates the birthdays of George Washington and Abraham Lincoln.
- Memorial Day (Last Monday in May): Honors those who died in military service.
- Independence Day (July 4): Celebrates the Declaration of Independence.
- Labor Day (First Monday in September): Honors the contributions of workers.
- Columbus Day (Second Monday in October): Commemorates the arrival of Christopher Columbus in the Americas.
- Veterans Day (November 11): Honors all veterans of the U.S. armed forces.
- Thanksgiving Day (Fourth Thursday in November): A traditional holiday celebrating the harvest and giving thanks.
- Christmas Day (December 25): Celebrates the birth of Jesus Christ.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between the Gregorian calendar and the Julian calendar?
The Gregorian calendar is more accurate than the Julian calendar due to its more precise leap year system. The Julian calendar overestimated the length of a year, leading to a discrepancy of approximately 11 minutes, causing the calendar year to drift from the actual solar year. The Gregorian calendar addressed this drift by introducing a more accurate leap year system.
2. How does the leap year system work in the Gregorian calendar?
A leap year occurs every four years, with the exception of years divisible by 100 but not by 400. This system ensures that the calendar year remains synchronized with the solar year.
3. Why are there different time zones in the United States?
The United States spans multiple time zones due to its vast geographical expanse. To ensure that the sun is at its highest point at noon across the country, different regions have been assigned different standard times.
4. What are some of the most significant holidays observed in the United States?
The United States observes numerous holidays throughout the year, including New Year’s Day, Martin Luther King Jr. Day, Presidents’ Day, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Columbus Day, Veterans Day, Thanksgiving Day, and Christmas Day.
5. How does the calendar affect everyday life in the United States?
The calendar plays a pivotal role in American society, influencing various aspects of life, including government and legal systems, business and commerce, education, personal schedules, and cultural events.
Tips for Using the Calendar Effectively
- Utilize digital calendars: Digital calendars offer features like reminders, notifications, and scheduling tools, making it easier to manage your time.
- Create a weekly schedule: Dedicate time each week to plan and organize your activities.
- Set realistic goals: Avoid overloading your calendar with too many commitments.
- Take breaks: Schedule regular breaks throughout the day to avoid burnout.
- Review and adjust: Regularly review your calendar and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
The calendar in the United States plays a vital role in organizing our lives, from personal schedules to national events. The Gregorian calendar, with its accurate leap year system and familiar structure, provides a framework for managing time and coordinating activities. Understanding the calendar’s history, structure, and significance is crucial for navigating American society effectively. By utilizing the calendar wisely, individuals and organizations can optimize their time, enhance productivity, and participate fully in the rich tapestry of American culture.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Calendar in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!