Understanding the Honey Calendar: A Guide to Beekeeping Success
Related Articles: Understanding the Honey Calendar: A Guide to Beekeeping Success
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Honey Calendar: A Guide to Beekeeping Success. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Honey Calendar: A Guide to Beekeeping Success

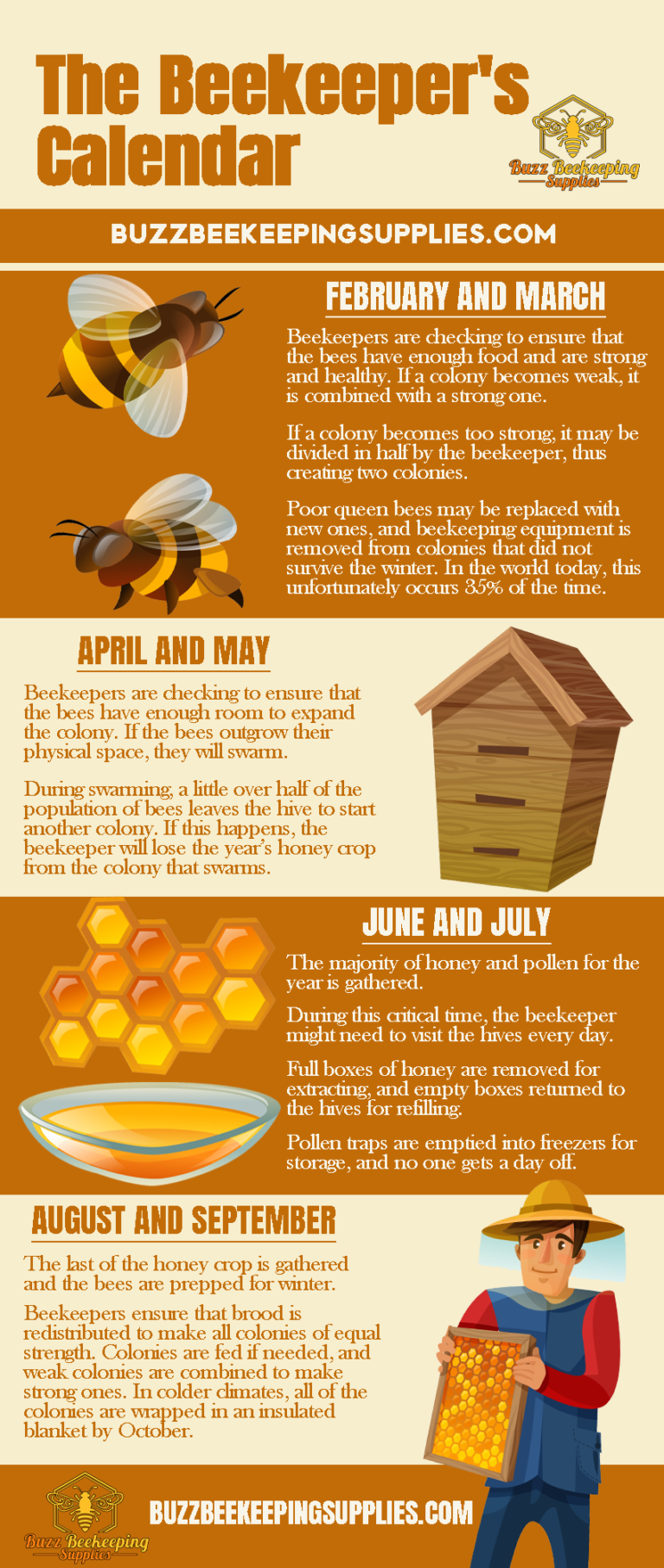
Beekeeping, a practice deeply intertwined with nature’s rhythms, relies heavily on understanding the intricate life cycle of honeybees. The "honey calendar," a valuable tool for beekeepers, provides a framework for tracking the seasonal activities of honeybees and aligning beekeeping practices with these natural cycles. This calendar, a compilation of observations and experiences spanning generations, helps beekeepers optimize hive management, maximize honey production, and ensure the health and well-being of their colonies.
The Honey Calendar: A Framework for Beekeeping
The honey calendar serves as a roadmap for beekeepers, outlining key events in the life cycle of honeybees throughout the year. This calendar is not a rigid blueprint but rather a flexible guide that adapts to local climate conditions and specific bee breeds.
Spring: A Time of Renewal and Growth
Spring marks the awakening of the hive after the winter dormancy. As temperatures rise and flowers bloom, the queen bee resumes egg-laying, initiating a period of rapid colony growth. This period demands careful attention from the beekeeper:
- Early Spring Inspection: Assessing the hive’s health, checking for sufficient food reserves, and ensuring the queen is laying well.
- Queen Introduction: If necessary, introducing a new queen to replace an aging or failing one.
- Disease and Pest Control: Monitoring for signs of diseases and parasites and implementing appropriate treatments.
- Expansion and Hive Management: Providing additional space as the colony grows and managing the brood nest to ensure optimal development.
Summer: The Season of Honey Production
Summer is the peak season for honey production, a time when honeybee activity reaches its zenith. The beekeeper’s focus shifts towards maximizing honey yields while maintaining colony health:
- Honey Flow Management: Understanding the local nectar flow, adjusting hive space to accommodate honey storage, and harvesting honey at the optimal time.
- Swarm Prevention: Identifying and managing swarming instincts, ensuring the colony remains strong and productive.
- Queen Excluder: Using queen excluders to restrict the queen to the brood nest, allowing for honey storage in the supers.
- Feeding and Water: Providing supplemental feeding if necessary and ensuring access to clean water sources.
Fall: Preparation for Winter
As the days shorten and temperatures drop, the hive enters a period of preparation for winter. The beekeeper’s role becomes crucial in ensuring the colony’s survival:
- Fall Inspection: Checking for sufficient food reserves, assessing the health of the colony, and treating for varroa mites.
- Feeding: Providing adequate winter stores of sugar syrup or pollen patties to sustain the colony throughout the cold months.
- Hive Preparation: Making necessary repairs to the hive and ensuring proper insulation for winter protection.
- Winterizing: Preparing the hive for winter by reducing the entrance size and protecting it from the elements.
Winter: A Time of Dormancy
Winter is a period of dormancy for honeybees. While the colony remains alive, activity is minimal, with the bees clustered together for warmth and conserving energy. The beekeeper’s role during this time is primarily observational:
- Minimal Disturbance: Avoiding unnecessary hive inspections to minimize stress on the colony.
- Monitoring for Signs of Distress: Keeping an eye on the hive for signs of distress, such as excessive drone production or a lack of activity.
- Protecting from Extreme Weather: Ensuring the hive is protected from harsh weather conditions.
Benefits of Using a Honey Calendar
Utilizing a honey calendar offers numerous benefits for beekeepers:
- Improved Hive Management: By understanding the seasonal activities of honeybees, beekeepers can make informed decisions regarding hive inspections, feeding, and other management practices.
- Enhanced Honey Production: By aligning beekeeping practices with the honey flow, beekeepers can maximize honey yields and ensure a successful harvest.
- Increased Colony Health: By proactively addressing potential threats and providing appropriate care, beekeepers can improve the overall health and longevity of their colonies.
- Reduced Stress on Bees: By understanding the natural rhythms of honeybees, beekeepers can avoid unnecessary disturbances and minimize stress on the colony.
- Increased Beekeeping Success: The honey calendar provides a framework for beekeepers to build a strong foundation for success, increasing their chances of thriving in the beekeeping world.
FAQs Regarding the Honey Calendar
Q: How do I create a honey calendar for my region?
A: A honey calendar should be tailored to the specific climate and beekeeping practices of your region. Consult with experienced local beekeepers, research your local flora and fauna, and observe the honey flow patterns in your area.
Q: What are the key events to include in a honey calendar?
A: Key events include the start and end of the honey flow, swarming season, queen introduction, disease and pest control measures, and winterization preparations.
Q: How often should I adjust my honey calendar?
A: It is recommended to adjust your honey calendar annually based on your observations and any changes in local conditions.
Q: What are some resources for creating a honey calendar?
A: Local beekeeping associations, online beekeeping forums, and books on beekeeping practices offer valuable resources for creating a customized honey calendar.
Tips for Using a Honey Calendar
- Record your observations: Keep detailed records of your hive inspections, honey production, and any other relevant information.
- Be flexible: The honey calendar is a guide, not a rigid rule. Adapt it to your specific needs and local conditions.
- Stay informed: Attend beekeeping workshops, read beekeeping publications, and stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices.
- Consult with experienced beekeepers: Seek advice from experienced local beekeepers for guidance and insights specific to your region.
Conclusion
The honey calendar serves as a vital tool for beekeepers, providing a framework for understanding the intricate life cycle of honeybees and aligning beekeeping practices with these natural rhythms. By understanding and utilizing this calendar, beekeepers can improve hive management, enhance honey production, and ensure the health and well-being of their colonies. The honey calendar is a testament to the deep connection between beekeepers and the natural world, a connection that fosters a sustainable and rewarding relationship with these essential pollinators.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Honey Calendar: A Guide to Beekeeping Success. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!